The four steps to become a registered psychologist with a specialised area of practice.

We've tried to make the complex clear and simple. There are many pathways to becoming a psychologist in Australia, each with different levels of educational investment and varying qualification outcomes. From before you commence university study until you're in the field as a fully qualified practitioner, here's what's required.
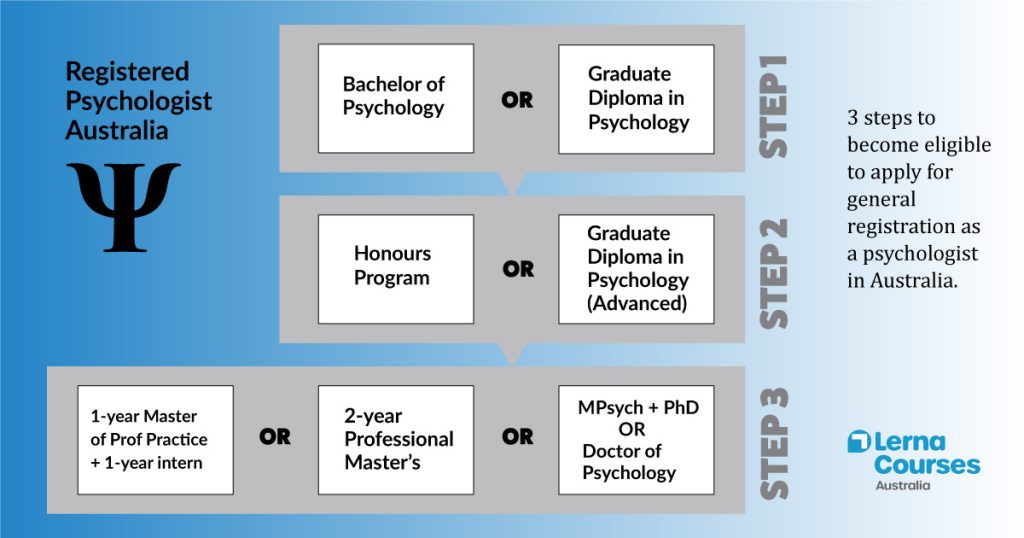
Step 1: Earn a Psychology Degree
You need a bachelor degree to eventually become a psychologist. If you don't have a university degree, enroll in a degree that allows you to major in Psychology. If you already have a degree in another field, go for a Graduate Diploma instead. The program must be APAC accredited.
Types of bachelor degrees
Based on the supply of programs from Australian universities, these are the 12 most popular kinds of psychology bachelor degrees. Most are 3-year programs. Double degrees (such as psychology and business) may require at least an extra year of study.
- Bachelor of Psychological Science
- Bachelor of Arts (Psychology)
- Bachelor of Science (Psychology)
- Bachelor of Psychological Science and Criminology
- Bachelor of Psychology
- Bachelor of Psychological Science/Bachelor of Laws
- Bachelor of Psychological Science/Bachelor of Business
- Bachelor of Nursing/Bachelor of Psychological Science
- Bachelor of Psychological Science and Counselling
- Bachelor of Social Science (Psychology)
- Bachelor of Behavioural Science (Psychology)
- Bachelor of Health Sciences (Psychology)
What if I already have a degree?
For university graduates from other fields, you don't have to complete another bachelor's degree. Instead, you can study for a Graduate Diploma in Psychology (or Graduate Diploma in Psychological Science). In professional terms, this is equivalent to a psychology bachelor degree.
The advantage of a Graduate Diploma in Psychology is that it is shorter and more focused. Participants complete only 10 subjects, much less than the 24 subjects contained in undergraduate programs. The qualification can be earned online in 20 months of part-time study.
Related: How to Become a Therapist in Australia
Step 2: Complete the Fourth Year
The second step is to extend your studies into a "fourth year". Graduates with high grades are invited by the university to do a psychology honours year. Alternatively, you can apply to do a Graduate Diploma in Psychology (Advanced), which also counts as the fourth year. Expect that around half of your fourth-year course will involve writing a dissertation or completing major research projects.
Grades required for honours
What GPA do you need? A Grade Point Average (GPA) of 5.5 or Weighted Average Mark (WAM) of 75% will normally be sufficient to be accepted in an honours or advanced graduate diploma program. This corresponds with half or more of your grades being Distinctions or High Distinctions. Some universities set slightly lower entry requirements than this.
Is honours difficult?
Honours is harder than undergraduate studies as it is designed for the better students aiming to become psychologists. However, most participants make it through with First-Class Honours or Second-Class, Upper Level, which are sufficient to continue in the field. The program aims to develop research skills and will require you to work independently at times.
Related: 4th Year Psychology Online Courses
Step 3: Choose a Postgraduate Degree
To become a psychologist in Australia, you need further academic qualifications after the fourth year. Once you enroll in a postgraduate psychology program, you can apply for provisional registration. This lets you gain practical experience as part of studying and training.
There are four main educational paths, each accredited by the Australian Psychology Accreditation Council (APAC). All lead to eligibility for full registration as a psychologist. For 2-year Master's and doctorates, you must also select the type of psychologist you want to become in your specialisation.
1-year Master of Professional Psychology
This is the quickest way into the psychology profession. The course lasts one year. It covers broad psychology principles through coursework and placements. After finishing, graduates do a year-long paid internship. This "5+1" pathway leads to general psychologist registration.
- Pros: Fastest route to registration.
- Cons: Does not integrate area of practice endorsement.
Related: Masters of Professional Psychology Online
2-year Master of Psychology
This program allows specialisation in areas like clinical or counselling psychology. It lasts two years. The program mixes coursework, practical placements, and a research project. It prepares students for specialised roles. Completion and supervised practice lead to psychologist registration.
- Pros: Facilitates specialisation. Potential for practice endorsement.
- Cons: More time and money required. Longer until earning a psychologist's salary.
Related: Master of Psychology Courses in Australia
Doctor of Psychology (PsyD)
The PsyD takes 3.5 to 4 years. It focuses on advanced clinical practice. The program includes intensive clinical training, coursework, placements, and a professional research project.
- Pros: In-depth clinical training. Leads to registration and potential endorsement.
- Cons: Time-consuming and costly. However, it offers broad career options in clinical settings and academia, similar to a PhD.
Doctor of Philosophy in Clinical Psychology (PhD)
A 4 to 4.5-year research-focused degree. It suits those combining clinical practice with research. The PhD is often pursued after at least the first year of a Master in Clinical Psychology. It prepares for roles in clinical practice, academia, and research. Publishing is a key component.
- Pros: Highest level of academic and research training. Suitable for academia, research, and advanced clinical practice.
- Cons: Most demanding in time and finances. Yet, it opens up opportunities equivalent to those of a PsyD, with a strong research and academic orientation.
Step 4: Gain Initial Experience as a Psychologist
Each degree is followed by an initial period of supervised practice to establish yourself as a psychologist.
- For graduates of a 1-year Master of Professional Psychology, this involves an internship year working as a provisional psychologist. You must also pass the national psychology exam.
- For the longer degrees, you graduate eligible for general registration as a psychologist. However, up to 2 years of supervised practice is required to be eligible for endorsement in the area of practice in which you have been specialising (less for doctorates).
Become a specialist
Area of practice endorsement is not the only key to specialisation. Most psychologists in Australia are registered psychologists without any endorsements who nonetheless specialise in fields such as counselling, Christianity, family, psychotherapy, relationships, school, etc. They specialise by accumulating work experience in a sector.
To work in hospitals and other clinical treatment settings, you do normally need endorsement in Clinical Psychology or Neuropsychology. The other areas with protected titles are Community, Counselling, Educational and Developmental, Forensic, Health, Organisational, and Sport and Exercise Psychology.